Java IO
Java IO流
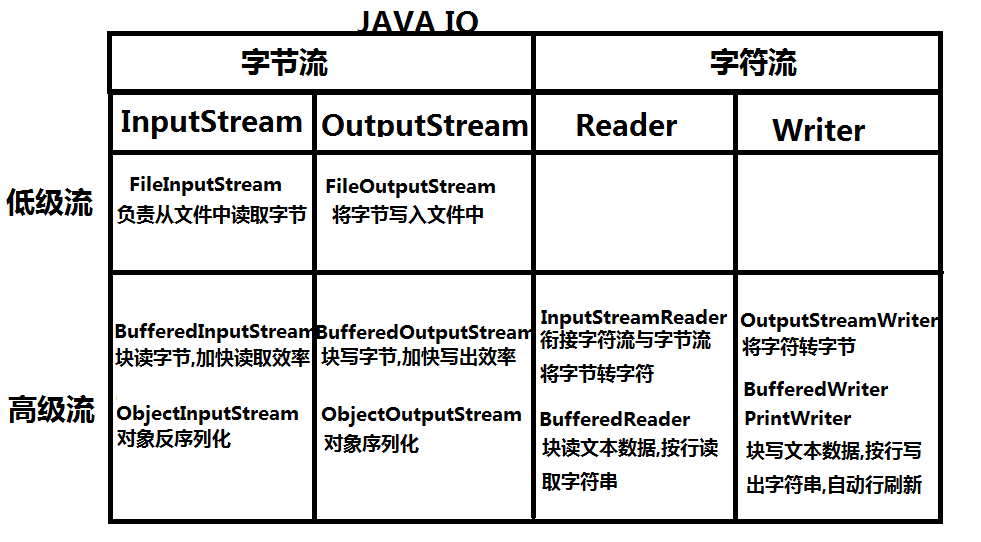
分类
java按照将流连接类型分为
- 节点流(低级流):是实际连接数据源与程序的“管道”,负责实际读写数据的流,读写一定是建立在节点流的基础上进行的
- 处理流(高级流):不能独立存在,必须连接在其他流上,目的是当数据“流经”当前流时对其进行加工处理,简化我们读写时对数据的相应操作
按流的方向分为
- 输入流:InputStream
- 输出流:OutputStream (所有字节流的超类)
按照处理字节单位分为
- 字节流:InputStream和OutputStream
- 字符流:Reader和Writer
常用的IO流:
- 文件流 FileOutputStream(路径/File对象)-FIS 和FileInputStream(路径/File对象)-FOS
- 对象流 ObjectOutputStream(fos)-OOS 和ObjectInputStream(fis)-OIS
- 字节缓冲流 BufferedOutputStream(fos)-BOS 和BufferedInputStream(fos)-BIS
- 字符转换流 OutputStreamWriter(fos)-OSW 和InputStreamReader(fis)-ISR
- 字符缓冲流 BufferedWriter(osw)-BW 和BufferedReader(isr)-BR
- 字符缓冲加速流 PrintWriter(bw)-PW
1. 文件流
- java.io.FileInputStream
- java.io.FileOutputStream
常用的一类低级流的实现类,用来来接文件
对文件进行读写操作(功能上与RAF一致,但都有各自的优缺点)
文件输入流的常用构造方法
- FileInputStream(File file)
FileOutputStream(String path)
上面两种构造方法创建的文件输入流为覆盖模式
即:若文件存在则文件数据清除,然后通过当前流写入的数据作为新数据保存- FileOutputStream(File file,boolean append)
- FileOutputStream(String path,boolean append)
以上两种构造方法创建的文件输入流为追加模式
即:若文件存在,则数据保留,当前流写入的内容会顺序追加到文件末尾
示例1 利用文件输出流写文件
package io;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FOSDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("./fos.txt",true);
String line = "记得双击嬷嬷哒";
byte[] data = line.getBytes("gbk");
fos.write(data);
System.out.println("写入完毕");
fos.close();
}
}示例2 利用文件输入流读文件
package io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 文件输入流,用于读取文件数据
*
* 文件流与RAF放入区别
* 1:RAF是基于指针的随机读写,读写方式更灵活
* 并且可以对文件部分内容覆盖进行编辑操作
* 而文件流则不行,文件流是基于java标准IO
* 的操作方式,而IO读写为顺序读写,
* 即只能向后读写操作不能回退
*
* 2:文件流可以借助流连接完成复杂
* 读写操作,这一点是RAF做不到的
* @author QAIU
*
*/
public class FISDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("fos.txt");
byte[] data = new byte[100];
int len = fis.read(data);
System.out.println("实际读取到了:"+len+"字节");
/*
* String(byte[] data,int offset,int len,string csn)
* 将给定的字符数组中
* 将给定字符数组从下标offset
* 处的连续len个字节按照指定的字符集转为字符串
*/
String line = new String(data,0,len,"gbk");
System.out.println(line);
}
}示例3 复制文件
package io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
使用文件流完成文件复制操作
@author QAIU
public class CopyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
1.创建文件输入流读取源文件
2.创建文件输出流写复制文件
3.循环读写,完成复制
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("\\jdk api 1.8_China");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("out.exe");
byte[] data = new byte[102];
int len = -1;
while((len = fis.read(data))!=-1) {
fos.write(data, 0, len);
}
System.out.println("复制完毕");
}
}2. 字节缓冲流
- java.io.BufferedOutputStream
- java.io.BufferedInputStream
缓存字节输入输出流 是一对高级流,
在流连接的作用是提高读写效率(内部维护了一个8K的字节数组,
并将读写的数据转换成块读写从而提高效率)
使用缓冲流复制文件
package io;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CopyDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\jdk api 1.8_China\\使用说明.docx");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("使用说明1.docx");
BufferedInputStream bif = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
int data = -1;
while((data = bif.read())!=-1) {
bos.write(data);
}
System.out.println("复制完毕!");
bif.close();
bos.close();
}
}3. 对象流
java.io.ObjectOutputStream
java.io.ObjectInputStream
对象流是一对高级流,作用是将java对象与字节
进行相互转换,便于我们读写java对象
对象输出流提供的方法:
void writeObject(Object obj)
将对象按照其结构转换一组字节并写出
写出对象所属的类必须实现Serializable接口
否则写出时会抛出异常
一个对象转出字节后会发现比该对象实际存储的数据要大
这是因为这组字节除了包含当前对象的数据外 还要记录对象的
结构信息以便于还原
这里涉及到两个专业术语:
- 将一个对象经过对象流写出时,对象流会按照其结构将该对象转换成一组字节,这个过程叫做对象序列化
- 这组被序列化后的字节在经过文件流写入文件(写入磁盘)做长久保存的过程 叫做数据持久化
对象输出流示例
Person.java:
package io;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 使用当前类实例测试 对象流的读写操作
* @author QAIU
*/
public class Person implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String name;
private int age;
private String gender;
private transient String[] otherInfo;
public Person(String name, int age, String gender, String[] otherInfo) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
this.otherInfo = otherInfo;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public String[] getOtherInfo() {
return otherInfo;
}
public void setOtherInfo(String[] otherInfo) {
this.otherInfo = otherInfo;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name+","+age+","+gender+","+Arrays.toString(otherInfo);
}
}OOSDemo.java:
package io;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class OOSDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String name = "小坤坤";
int age = 18;
String gender = "男";
String[] outerInfo = {"学生","中国","喜欢唱跳篮球rap"};
Person p = new Person(name, age, gender, outerInfo);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("person.obj");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(p);
System.out.println("写出完毕");
oos.close();
}
}使用对象输入流 反序列化
package io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class OISDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("person.obj");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
Object object = ois.readObject();
System.out.println(object);
ois.close();
}
}4. 转换流
java将按照读写单位分为:字节流和字符流
字节流:以字节为单位,一次至少读写8位二进制
字符流:以字符为单位读写数据,由实际读写的字节量与
指定的字符集与读写的字符数据有关 但是在java内部表示字符数据时都是用char表示(2字节)
- java.io.Writer
- java.io.Reader
上面两个类是抽象类,是所有字符输出流和字符输入流的超类
里面规定了读写字符相关的方法
转换流(字节流转字符流),他们是字符流的一对常用实现类,是一对高级流
实际开发中我们在读写文本数据时,它们是流连接中重要的一环
但是我们不会直接操
Java提供了这样一对转换流
- OutputStreamWriter: 是字符流通向字节流的桥梁
- InputStreamReader: 从字节流到字符流的桥梁
使用转换输出流写文本信息
package io;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class OSWDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("osw.txt");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"gbk");
/*
* 转换流在创建时通过指定第二个参数来确
* 定字符集,这样通过当前流写出文本时
* 都会按照该字符集转换为字节后再做写出
*/
String string = "是兄弟就来砍我~~~~~~";
osw.write(string);
osw.close();
System.out.println("输出完毕");
}
}使用转换输入流读文本信息
package io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
* java.io.InputStreamReader
* 转换流--输入
*
* InputStreamReader与OutputStreamWriter之所以
* 称为转换流是因为:
* 通常java中其他的高级字符流都只能连接在其他字符
* 流上,都不能直接连接字节流.但是它们是可以连接在
* 字节流上的,而本身又是字符流,这样就可以让其他的
* 字符流与字节流衔接了,起到了"转换器"的作用.
*
* @author QAIU
*
*/
public class ISRDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("./src/io/ISRDemo.java");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
int d = -1;
while((d = isr.read())!=-1) {
System.out.print((char)d);
}
isr.close();
}
}5. 字符缓冲流和缓冲加速(字符打印)流
- java.io.BufferedWriter
- java.io.BufferedReader
以上两个就是缓冲字符输入与输出流是一对高级流,内部有缓冲区,读写文本数据效率高
- java.io.PrintWriter
内部总是连接BufferedWriter作为缓冲加速使用
并且PW还支持自动刷新功能,实际开发比较常用
PrintWriter提供了对文件直接写操作的构造器
- PrintWriter(File file)
- PrintWriter(String path)
并且上面的构造器还支持一个重载PrintWriter(String fileName, String csn),第二个参数
是字符集名称,这样可以按照指定的字符集名称写出文本数据
使用缓冲字符输入流读取文件
package io;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
* 缓冲字符输入流
* 特点:块读写效率高,并且可以按行读取字符串
* @author QAIU
*
*/
public class BRDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("./src/io/BRDemo.java");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
/*
* String readline()
* 返回一行字符串,缓冲流会将一行字符串
* (到换行符"\n"为止,但不包括"\n")的内容
* 返回,若返回值为null,则表示流已经读取到了末尾
*/
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine())!=null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}
}使用字符打印流写文件
package io;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class PWDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("pw.txt","GBK");
pw.println("写入换行");
pw.print("不换行");
pw.println("换行了");
pw.close();
}
}在流连接中使用PW
package io;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class PWDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("pw2.txt");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(bw);
pw.println(123*3);
pw.close();
}
}缓冲输出流的缓冲区问题
package io;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class BOS_flushDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("bos.txt");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
String str = "测试文本";
bos.write(str.getBytes("GBK"));
/*
* void flush()
* 该方法是OutputStream定义的方法,
* 但并非所有字节输出流都实现了该方法的功能
* 只有缓冲流的该方法有实际意义
* 作用是一次性将缓冲区已存在的数据写出
* 之所以所有的字节流都有该方法是因为
* 流连接应用中缓冲流通常不是"终端流"(直接被我们操作的流)
* 为了传递刷新缓冲区功能才有
*/
bos.flush();
System.out.println("写入完毕");
bos.close();
}
}综合应用 简易记事本工具
package io;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 简易记事本工具
* 程序启动后要求用户输入文件名,之后将用户输入
* 的每一行字符串按行写入该文件,单独输入exit
* 时退出
* 使用PW完成按行写入文本数据操作
* 要求 独立完成流连接操作
* @author QAIU
*
*/
public class Note {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入文件名");
String filename = scanner.nextLine();
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(
new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream(filename),"gbk")),true);
System.out.println("请输入每一行文本,按exit退出");
String str;
while(!"exit".equals(str = scanner.nextLine())) {
pw.println(str);
}
pw.close();
System.out.println("已退出,欢迎下次使用");
}
}